Global trade refers to the commercial transactions involving the exchange of goods and services across international borders. The present article provides a comprehensive elucidation of global trade, encompassing its fundamental constituents, operational methodologies, and challenges. The objective of this article is to provide informative content that enriches one’s comprehension of international commerce and its impact on the global economy.
Understanding Global Trade.

The term global trade pertains to the exchange of goods and services across international borders. The global distribution of goods and services is influenced by variations in demand across nations and disparities in resource endowments and production capacities across regions. The phenomenon of global trade encompasses diverse modalities such as the outbound and inbound movement of commodities, amenities, and intangible assets, alongside cross-border capital investment and offshore subcontracting.
Key Players in Global Trade.

The phenomenon of global trade encompasses a multitude of actors, such as governmental entities, commercial enterprises, and individuals who purchase goods and services. The following is a concise summary of the principal actors involved in international trade.
Governments:
The establishment of trade policies, regulations, and agreements with other nations is a critical function of governments in the realm of global trade. In addition, they are responsible for upholding trade regulations, imposing tariffs and embargoes, and engaging in diplomatic negotiations to safeguard their country’s welfare and foster financial advancement.
Businesses:
Enterprises are the principal catalysts of global trade, as they manufacture and vend commodities and amenities across various nations. International trade is pursued by businesses to expand their market reach, leverage global supply chains, and capitalise on cost disparities and competitive strengths across various nations.
Consumers:
The access to a diverse range of goods and services from different parts of the world is a significant advantage of global trade for consumers, making them the ultimate beneficiaries. The phenomenon of global trade leads to advantages such as heightened competition, decreased pricing, and expanded options for consumers.
How Does Global Trade Work? – Comprehensive Guide!
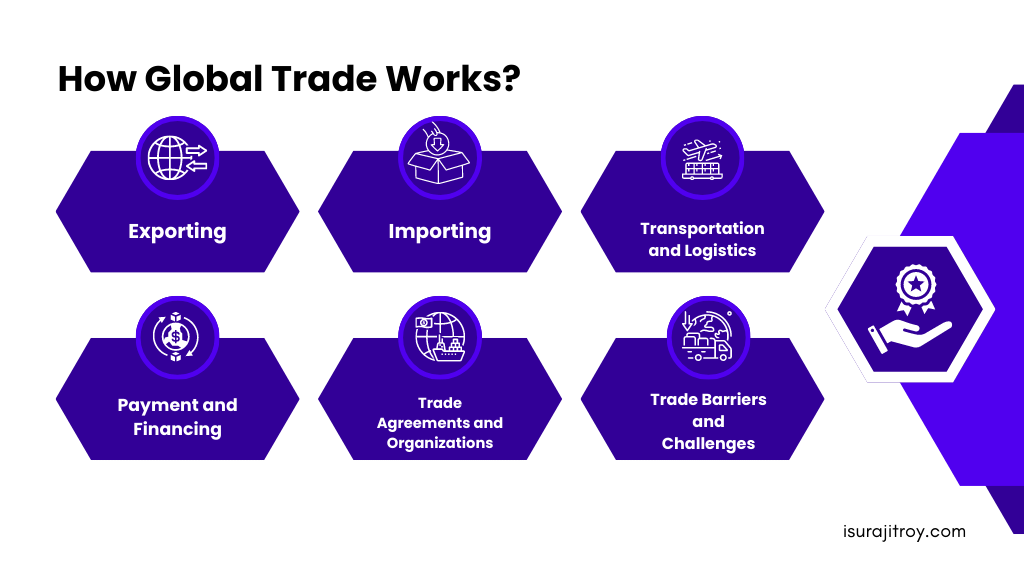
The concept of global trade encompasses a multifaceted system of exchanges and interconnections among purchasers and vendors situated in various nations. The following is a systematic outline of the functioning of global trade.
Exporting:
Exporting is the act of vending commodities or amenities that are manufactured in a particular nation to purchasers located in a different nation. Exporters are required to adhere to diverse export regulations, which entail securing the requisite licences and permits, and producing the mandatory documentation, such as commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin.
Importing:
The act of purchasing commodities or amenities that are manufactured in a foreign nation and transporting them to one’s domestic territory is commonly known as importing. Importers are required to adhere to multiple import regulations, which encompass the payment of customs duties, taxes, and fees, as well as the fulfilment of import licencing prerequisites.
Transportation and Logistics:
The transportation and logistics sectors are essential components of international trade, as they facilitate the transportation of commodities and services across international boundaries. The aforementioned encompasses the conveyance of commodities through various modes of transportation, namely air, sea, road, or rail, in addition to the administration of logistical operations, such as stockpiling, inventory control, and the process of customs clearance.
Payment and Financing:
The transfer of funds between buyers and sellers in different countries is a crucial aspect of global trade, encompassing payment and financing as essential components. The aforementioned comprises a range of payment modalities, encompassing letters of credit, bank transfers, and trade finance instruments, in addition to currency exchange and risk mitigation.
Trade Agreements and Organizations:
Trade agreements and organisations exert a substantial influence on the configuration of global trade by instituting norms, guidelines, and benchmarks for transnational commerce. Trade agreements encompass a variety of arrangements, such as the World Trade Organisation (WTO), regional trade agreements, such as the United States Mexico Canada Agreement (USMCA), and bilateral trade agreements between nations.
Trade Barriers and Challenges:
The phenomenon of global trade encounters a multitude of obstacles and impediments, encompassing trade barriers in the form of tariffs, quotas, and non-tariff barriers, alongside geopolitical tensions, currency fluctuations, trade disputes, and environmental and social considerations.
Trade Finance and Insurance.
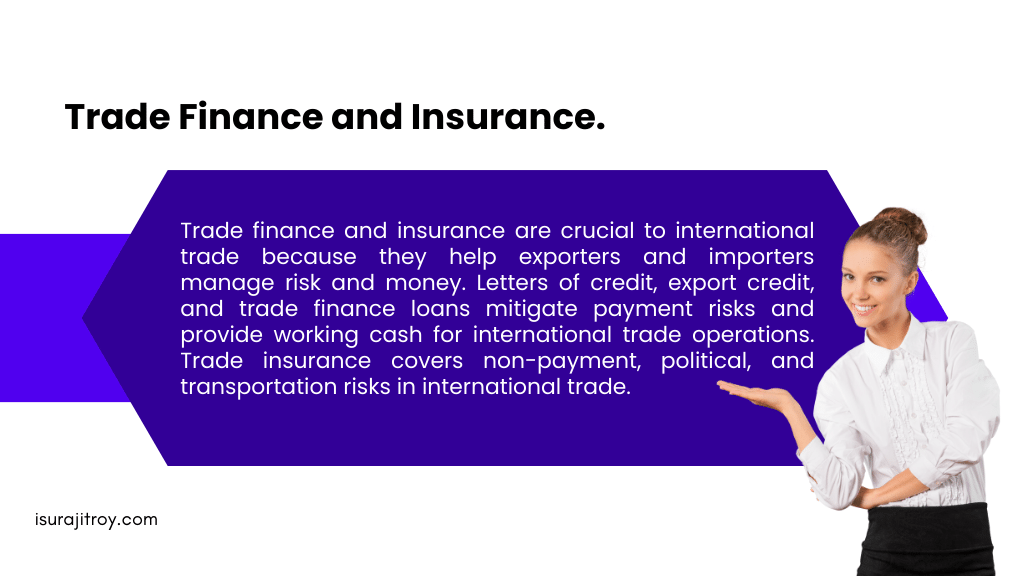
The provision of financial assistance and risk management to exporters and importers is of paramount importance in the realm of international trade, with trade finance and insurance playing pivotal roles in this regard. Trade finance encompasses a range of financial instruments, including letters of credit, export credit, and trade finance loans, that serve to facilitate international trade transactions by mitigating payment risks and providing working capital. Trade insurance offers coverage against various risks that may arise during global trade transactions, including non-payment, political risks, and transportation risks.
Global Supply Chains.

Global supply chains are complex systems of manufacturing and delivery that extend across numerous nations. The process entails the transfer of commodities, amenities, and data from primary material providers to producers, intermediaries, and vendors across various nations.
The utilisation of global supply chains facilitates the acquisition of resources, labour, and markets across various regions of the world, thereby serving as a crucial factor in enhancing the effectiveness and competitiveness of international trade. Notwithstanding the benefits of global supply chains, they are also confronted with various impediments such as interruptions, tardiness, and hazards that can exert an influence on the movement of commodities and amenities across international boundaries.
The Impact of Global Trade.

The phenomenon of global trade exerts noteworthy effects on the economies, enterprises, and communities across the globe. The impact of global trade on different stakeholders can be analysed through several key factors.
Economic Growth:
The expansion of markets, heightened competition, and promotion of specialisation and efficiency in production are among the ways in which global trade can contribute to economic growth. Furthermore, it has the potential to foster job creation, yield tax income for governmental bodies, and promote advancements in innovation and technology transfer.
Business Opportunities:
Exploring Potential Business Ventures The phenomenon of global trade presents commercial enterprises with prospects to gain entry into novel markets, broaden their consumer pool, and leverage worldwide supply networks. Globalisation facilitates the procurement of raw materials and components from diverse nations, grants access to novel technologies and specialised knowledge, and broadens the customer base beyond domestic boundaries for commercial entities.
Advantages for Consumers:
The phenomenon of global trade confers advantages to consumers by affording them the opportunity to avail themselves of a diverse array of commodities and amenities sourced from various regions across the globe. The expansion of consumer options, reduction of prices via market competition, and enhancement of product quality and innovation are all observed outcomes.
International Relations:
The field of study concerned with the interactions and relationships between nations and other actors in the global political system is commonly referred to as international relations. The significance of “global trade” in international affairs is paramount, as it fosters economic collaboration, diplomatic ties, and cultural interchange among nations. Trade negotiations and agreements can serve as a means to resolve disputes and conflicts.
Sustainable Development:
The concept of sustainable development refers to the practise of meeting the needs of the present generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. The promotion of responsible business practises, environmental conservation, and social responsibility can be facilitated by global trade, thereby contributing to sustainable development. The implementation of fair trade practises and responsible supply chain management can contribute to the achievement of the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by mitigating poverty, inequality, and climate change.
Challenges and Controversies in Global Trade.

Although global trade offers numerous advantages, it is not without its obstacles and disputes. The subject of global trade is accompanied by several significant challenges and controversies.
Trade Barriers:
The imposition of trade barriers, including but not limited to tariffs, quotas, and non-tariff barriers, may impede the movement of commodities and amenities across international borders, thereby generating inequitable competition. Tariffs may result in trade disputes among nations and affect the movement of international trade.
Geopolitical Tensions:
Geopolitical tensions, encompassing trade disputes, sanctions, and political conflicts among nations, have the potential to impede “global trade” and engender ambiguity in the global business milieu. In addition, their influence can extend to the supply chains, production processes, and overall stability of international trade.
Environmental and Social Concerns:
The phenomenon of global trade has been observed to have detrimental effects on the environment and society, including but not limited to deforestation, pollution, labour exploitation, and human rights violations. The aforementioned apprehensions have resulted in heightened examination and governance in the realm of international commerce, emphasising the principles of sustainability, conscientious sourcing, and corporate social accountability.
Currency Fluctuations:
The impact of currency fluctuations on global trade can be observed through their influence on exchange rates, pricing, and the costs associated with goods and services. The generation of instability in cross-border commercial dealings, the potential influence on profit margins, and the introduction of hazards to enterprises involved in global trade are among the effects that can be produced.
Intellectual Property Rights:
The matter of intellectual property rights, encompassing patents, trademarks, and copyrights, has the potential to generate conflict in the context of international commerce. Safeguarding intellectual property rights is of paramount importance for enterprises involved in global trade as it serves to protect their innovations, commodities, and brand recognition. Intellectual property violations and conflicts may arise in the context of international commerce, resulting in legal disputes and controversies.
Emerging Technologies:
The implementation of novel technologies, such as e-commerce, blockchain, and automation, is revolutionising the international trade landscape by enhancing efficacy, transparency, and security. Nevertheless, the employment of these technologies poses certain hurdles, including but not limited to issues concerning data confidentiality, cybersecurity, and workforce displacement. Enterprises involved in international commerce must adjust to the evolving technological environment to maintain competitiveness and adherence to regulations.
Trade Agreements and Policies:
Trade agreements and policies, including but not limited to free trade agreements (FTAs) and customs regulations, exert a significant influence on the regulations and parameters of international trade. The policies may have an effect on tariffs, quotas, market entry, and regulatory obligations for enterprises involved in international commerce. Alterations in trade agreements and policies, coupled with transformations in geopolitical dynamics, have the potential to generate ambiguities and obstacles for enterprises functioning within the realm of global trade.
Conclusion.
To conclude, the phenomenon of global trade is a multifaceted and ever-evolving process that encompasses the transfer of commodities, amenities, and knowledge across international boundaries. International trade is a pivotal component of the worldwide economy, facilitating avenues for enterprises to broaden their market reach, acquire resources, and stimulate economic advancement. Notwithstanding its benefits, global trade encounters various obstacles and disputes, including impediments to trade, geopolitical frictions, ecological and societal apprehensions, currency volatility, intellectual property protections, nascent technologies, and modifications to trade accords and policies.